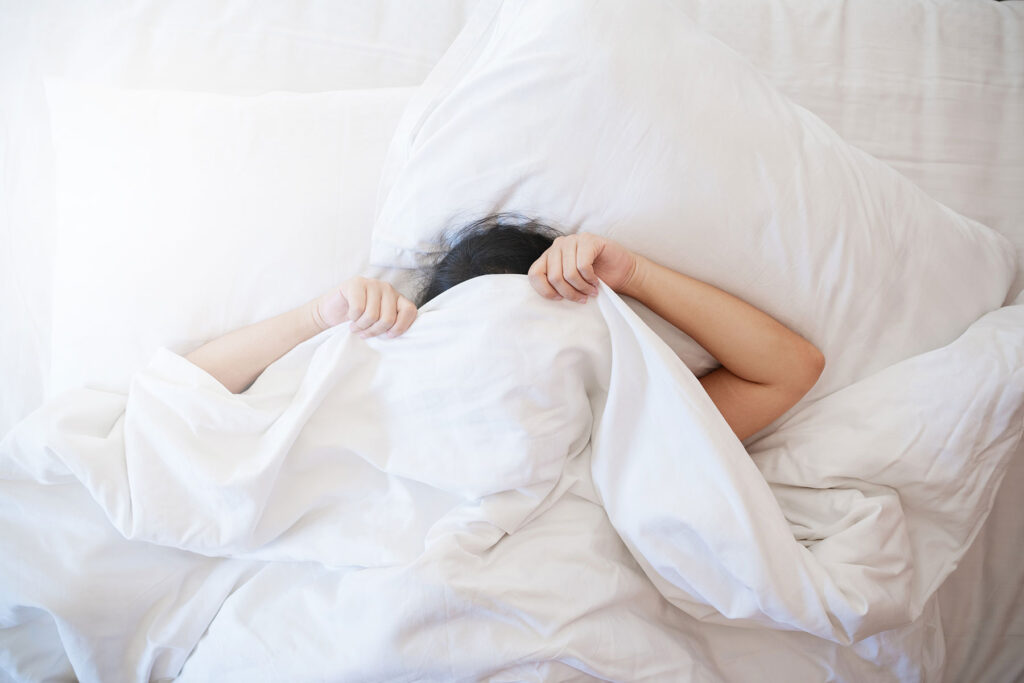
Muscle relaxers, also known as muscle relaxants, are medications prescribed by physicians to treat a range of physical issues. Some of these drugs have a potential for addiction and can result in withdrawal when stopped. The side effects of muscle-relaxing drugs can be risky. If you are concerned that a medication you are taking for muscle pain or spasms is affecting your functioning or that you are becoming physically dependent on it, consider seeking information and support from an addiction treatment center.
Promises Behavioral Health offers treatment for mental health and substance use disorders (SUDs). Do you have questions such as “Do muscle relaxers make you sleepy?” or “Do muscle relaxers make you spacey?” If so, don’t hesitate to call us at 844.875.5609 or submit this online form. If you want to discuss the possibility of dependence and addiction with one of our professional staff, that can be done in absolute confidentiality. Just call 844.875.5609 or use the Promises online contact form.
Muscle Relaxers – What Do They Do?
Muscle relaxers affect the function of muscles, including treating spasms, spasticity, and pain. There are two kinds of muscles in the body:
- Skeletal muscles – the ones you have control over that move your body
- Smooth muscles – muscles that function automatically, without input from you, like the muscles of the stomach and blood vessels
The majority of muscle relaxers are central nervous system depressants, having a sedative effect to prevent nerves from sending the wrong signals to the brain or from sending pain signals.
- Antispastics affect the spinal cord or the skeletal muscle to improve hypertonicity (muscle tightness) and involuntary spasms.
- Antispasmodics decrease muscle spasms by affecting the brain and spinal cord (central nervous system).
Muscle relaxers are used to treat:
- Cerebral palsy (CP)
- Spinal cord injury
- Stroke
- Multiple sclerosis (MS)
- Traumatic brain injury (TMI)
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
But sometimes, they are used to treat conditions unrelated to the action of muscles. For example, diazepam (Valium) is a muscle relaxant that is commonly used to treat anxiety.
Do Muscle Relaxers Make You Sleepy?
The drugs primarily used as muscle relaxers are typically depressants, and thus, the answer is, yes, they can make you sleepy. Short-term side effects are generally mild as long as the drug is used as prescribed. These can include the following:
- Sleepiness
- Dizziness
- Fatigue
- Headache
- Nausea
- Loss of concentration (spaciness)
- Mild to moderate sedation
Depending on what specific muscle relaxer is prescribed, the following are among the more severe side effects of this kind of drug:
- Confusion
- Tremors
- Weakness
- Insomnia
- Drug dependence
- Hallucinations
- Urinary and gastrointestinal issues
- Low blood pressure
If you experience any of the above side effects when using a muscle relaxer, call your doctor right away.
Addiction and Muscle Relaxers
Not all muscle-relaxing drugs put users at risk of dependence and addiction. Two are controlled substances, which means they have the ability to create physical dependence. They are carisoprodol (Soma) and diazepam (Valium). Anyone with a personal or family history of SUDs should ask their physician for a different medication to treat muscle pain, spasms, or spasticity.
Using muscle relaxers with other substances, such as alcohol or prescription painkillers, can greatly increase the side effects as well as the risk of abuse, dependence, and addiction. Approach the use of any prescription drug with caution and monitor your reactions and symptoms. If you have any concerns about the effects of a muscle relaxer on your well-being, contact Promises Behavioral Health to answer questions and provide support.
Call Promises Today for Help with Muscle Relaxer Abuse
Reach out to the staff at Promises to get solid information about the risks and side effects of muscle relaxers. Call us by dialing 844.875.5609 or simply fill out the Promises online contact form.